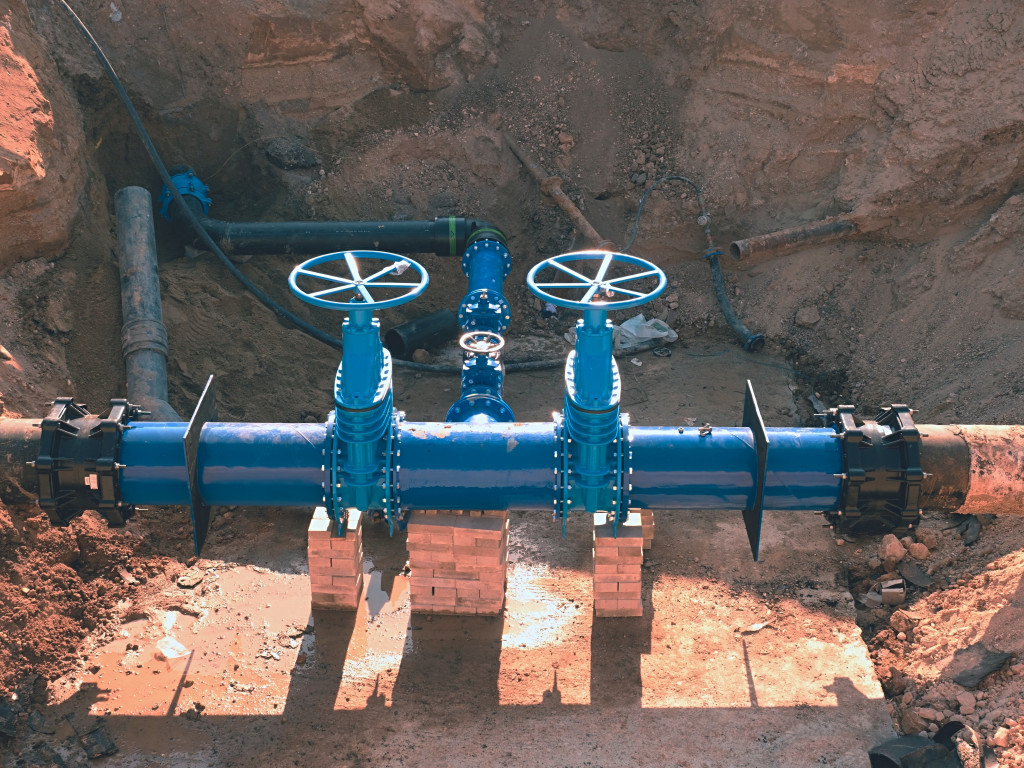
In a house plumbing system, different materials are utilized for potable water pipes and drain water pipes. Older homes often have many other lines, especially since the plumbing system has had numerous repairs or changes over the years. Don’t be surprised if your home only has a single material for all the water pipes. Below are some of the more frequently used materials.
CPVC
Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride is commonly referred to as CPVC. When present, the plastic is typically off-white or cream-colored. As long as the schedule does not call for temperatures higher than 180 degrees Fahrenheit (82.22 °C), this pipe can handle cold and hot water lines. Push-fit fittings like SharkBite, designed for use with copper and PEX, can also be utilized with CPVC piping.
A typical lifespan for CPVC and PVC pipes is approximately 50 to 75 years when kept under ideal conditions. However, early failure is also documented in some cases.
PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly utilized in various plumbing applications, such as drainage pipes and water mains. To ensure your drainage system withstands different elemental properties, ask your plumber to use OBIC products as the lining material. Aeration piping, building, and home supply piping are all typically made from the same material. One of the most prevalent plastics used in pools and spas is PVC. While white PVC pipe is the most common, you can also find it in various colors.
Most of the time, you can figure out what the pipe is used for by its markings and colors. For instance, reclaimed water is piped in purple with black writing. Moreover, PVC comes in various thicknesses, which are referred to as schedules. The most commonly used schedule for pipes in water distribution is Schedule 40.
Copper
In HVAC systems, refrigerant lines are often made from copper and distribute cold and hot water. Most states do not authorize this, even though it has historically been used in gas pipelines. In contrast to copper tubing, which can be used in above-ground and underground applications, it is critical to use a protective sleeve when piping underground.

Copper has long been the water supply pipe of choice for its high corrosion resistance and longevity. Galvanized steel has fallen out of favor due to its inferior corrosion resistance. Over time, copper thins out, which results in pinhole leaks. Various types of plastic, most recently PVC, have supplanted copper as the preferred material, but you can still find copper piping and fittings in the present. Because copper costs more and requires more labor for installation, many contractors have replaced the traditional water piping with PEX.
K, L, and M represent varying levels of copper thickness. In terms of thickness, M is the thinnest copper grade. For several methods to connect copper, there are sweat-soldering, push-fit fittings, and compression fittings.
Galvanized Steel
Galvanized pipe is a steel pipe coated with zinc, preventing corrosion inside the pipe as water consistently passes through. This type of pipe was formerly the most prevalent of the water supply pipes. Unfortunately, this practice has fallen out of favor because it takes more effort and time to cut, thread, and install a galvanized pipe. However, in bigger commercial applications, galvanized pipe is still used for the distribution of water.
Even if your house was built before the 1970s, it might still have galvanized water lines in it. House inspection organizations claim galvanized pipe can last for 40 to 50 years. Upgrading your plumbing system may be necessary if it is nearing the end of its lifespan. Many hardware stores provide different fittings of galvanized steel, and staff members can thread and cut your pipes to meet your needs.
PEX
Cross-linked polyethylene is abbreviated as PEX. Other times, people call it XLPEI. PEX has been utilized for both cold and hot lines in residential buildings and hydronic heating systems like systems with radiant under-floors.
While copper tends to have a lifespan of fewer than 50 years, PEX is estimated to have a life expectancy of more than that. The usage of PEX tubing has replaced copper and other polymers for water supply pipes for professional plumbers. It has a lower cost and is much easier to carry in the form of long rolls of tubing. Reduced elbows and other fittings, since the flexible tubing is easily bendable around the corners, dramatically speeds up installation.
Picking the appropriate plumbing pipe can be a tough decision because of the extensive range of materials available. Getting in touch with qualified plumbing engineers is the most effective approach for finding out about different plumbing materials and their benefits. Knowing the fundamentals of plumbing lets you make sure that your plumbing system employs the appropriate material for your budget and project requirements.